1. Introduction & Overview
In today’s fast-paced digital era, delivering software rapidly, securely, and reliably is a necessity. DevSecOps—an extension of DevOps with embedded security—demands automation at every stage of the software delivery lifecycle. That’s where CI/CD comes in.
What is CI/CD?
CI/CD refers to a set of practices and pipelines that enable development teams to:
- Continuously Integrate code into a shared repository
- Continuously Deliver (or deploy) that code to production or staging environments
Together, CI/CD enables faster releases, better collaboration, and built-in security in every step.
History / Background
- CI emerged in early 2000s (popularized by Extreme Programming) for merging changes frequently.
- CD evolved later as infrastructure-as-code and containerization matured.
- Over time, it became foundational for DevOps and DevSecOps cultures.
Why CI/CD in DevSecOps?
- Security Gates: Automate security scans in CI/CD pipelines.
- Shift-Left Testing: Detect security & quality issues early.
- Auditability: Every step is versioned and logged.
- Speed + Safety: Faster delivery with secure code quality.
2. Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| CI | Continuous Integration – merging code changes automatically & frequently |
| CD | Continuous Delivery/Deployment – delivering/deploying new versions regularly |
| Pipeline | Set of stages like build, test, scan, deploy automated via tools like GitHub Actions |
| Artifact | A compiled version (e.g., JAR, Docker image) ready to be deployed |
| Orchestration | Managing tasks across multiple systems (e.g., Kubernetes deployment) |
| Shift Left | Detecting issues earlier in the SDLC |
How CI/CD fits into DevSecOps Lifecycle
Plan → Code → Build → Test → Release → Deploy → Operate → Monitor
↑
CI/CD Pipeline (with embedded security)
- CI fits into: Code → Build → Test
- CD fits into: Release → Deploy → Operate
- DevSecOps integrates security checks at every transition
3. Architecture & How It Works
CI/CD Pipeline Components
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| Source Control | Code repository (e.g., GitHub, GitLab) |
| Build Server | Compiles code (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) |
| Test Framework | Runs automated unit, integration, security tests |
| Security Tools | SAST, DAST, secrets scanning (e.g., Snyk, SonarQube) |
| Artifact Store | Stores deployable files (e.g., Nexus, Artifactory) |
| Deployment Tool | Pushes builds to production (e.g., ArgoCD, Spinnaker) |
CI/CD Architecture Diagram (Descriptive)
[Developer]
↓ Push Code
[Git Repo (GitHub)]
↓ Webhook Trigger
[CI Server (Jenkins / GitHub Actions)]
↓
[Build → Test → Security Scan]
↓
[Artifact Registry (e.g., Docker Hub)]
↓
[CD Tool (e.g., ArgoCD)]
↓
[Dev / QA / Prod Environments (e.g., Kubernetes)]
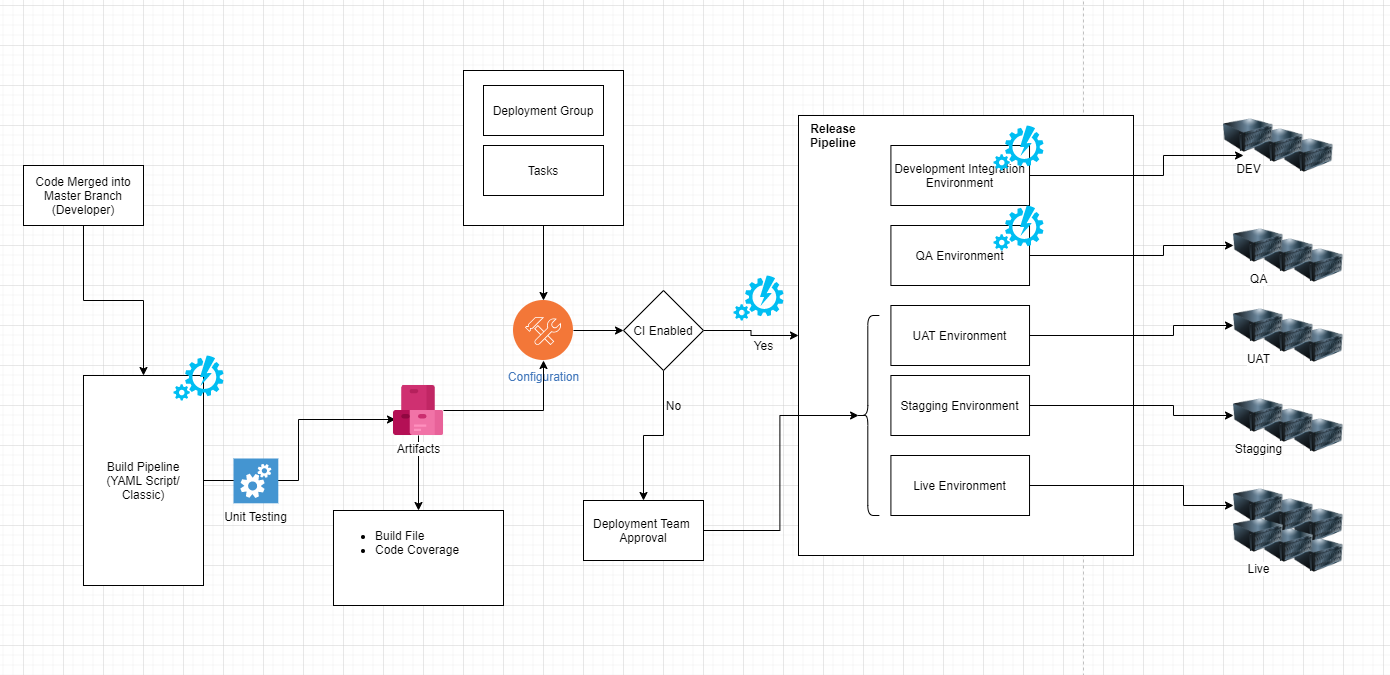
Integration Points
- GitHub/GitLab → Source control & CI trigger
- Docker/Kubernetes → Containerization & deployment
- Cloud (AWS/GCP/Azure) → Environments & infrastructure
- Security Scanners → Snyk, Trivy, SonarQube integrations
4. Installation & Getting Started
Prerequisites
- GitHub account
- Docker installed
- Kubernetes (Minikube or cloud cluster)
- Node.js project for demo
- GitHub Actions enabled
🛠️ Step-by-Step Setup (Using GitHub Actions)
Step 1: Create a GitHub Repo
mkdir ci-cd-demo && cd ci-cd-demo
git init
echo "# CI/CD Demo" > README.md
git add . && git commit -m "init"
Step 2: Add GitHub Actions Workflow (.github/workflows/main.yml)
name: CI/CD Pipeline
on: [push]
jobs:
build-and-deploy:
runs-on: ubuntu-latest
steps:
- name: Checkout code
uses: actions/checkout@v3
- name: Setup Node
uses: actions/setup-node@v4
with:
node-version: 18
- name: Install dependencies
run: npm install
- name: Run tests
run: npm test
- name: Security scan
uses: snyk/actions/node@master
env:
SNYK_TOKEN: ${{ secrets.SNYK_TOKEN }}
- name: Docker build and push
run: |
docker build -t myapp .
docker tag myapp mydockerhub/myapp:latest
docker push mydockerhub/myapp:latest
5. Real-World Use Cases
Use Case 1: Healthcare App
- Automated HIPAA compliance checks in the CI pipeline
- Secure deployment via CD into AWS with logging enabled
Use Case 2: E-commerce Platform
- CI pipeline runs vulnerability scans before every release
- Canary deployment using ArgoCD for high availability
Use Case 3: FinTech App
- Static and dynamic code analysis with GitHub Actions + OWASP ZAP
- Artifact signed and stored securely in a private repo
Use Case 4: DevSecOps Training Platform
- Multiple learners push to repo triggering shared CI/CD
- Feedback loop for security best practices included
6. Benefits & Limitations
✅ Key Benefits
- Faster time to market
- Embedded security in all stages
- Improved team collaboration
- Scalable, reproducible builds
⚠️ Common Challenges
- Complex configuration management
- Toolchain fragmentation
- Requires team-wide discipline
- Security scanning can slow down builds
7. Best Practices & Recommendations
🔐 Security Tips
- Use secrets manager instead of plaintext secrets
- Run security tests (SAST, DAST, dependency checks) on every commit
- Enable 2FA on CI/CD accounts
⚙️ Performance & Automation
- Cache dependencies for faster builds
- Automate rollback on failure
- Use lightweight containers for build agents
✅ Compliance Alignment
- Generate audit logs for every pipeline run
- Tag builds with metadata (e.g., Jira ticket, release note)
- Use policy-as-code for security gate enforcement
8. Comparison with Alternatives
| Tool/Approach | CI/CD Support | Security Integration | Learning Curve | Cloud Native |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Jenkins | High | Plugin-based (Snyk, SonarQube) | Medium | Partial |
| GitHub Actions | High | Native + third-party actions | Easy | Yes |
| GitLab CI | High | Native SAST/DAST | Medium | Yes |
| CircleCI | High | 3rd-party integrations | Low | Yes |
🔍 When to choose CI/CD (via GitHub Actions or Jenkins)?
- GitHub Actions for ease of use and GitHub-native projects
- Jenkins for complex workflows with plugin-based architecture
9. Conclusion
CI/CD is not just a DevOps enabler, but a DevSecOps powerhouse—integrating testing, compliance, and security directly into the software pipeline.
🔮 Future Trends
- AI in CI/CD for smarter test execution
- Policy-as-Code for security compliance
- Zero-trust deployments and supply chain validation