Introduction & Overview of C++
C++ is a powerful, high-level programming language developed by Bjarne Stroustrup in 1979. It is an extension of the C programming language with object-oriented programming features.
Key Features of C++
- Object-Oriented: C++ supports classes and objects, allowing for encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism.
- Performance: C++ allows low-level manipulation and direct memory access for high performance.
- Portability: C++ code can be compiled to run on various platforms.
- Standard Library: C++ provides a rich standard library for various operations and data structures.

Core Concepts & Terminology of C++
In C++, there are several key concepts and terminologies that are important to understand for developing applications effectively.
Object-Oriented Programming (OOP)
C++ is primarily an object-oriented programming language, which means it focuses on creating objects that interact with each other to achieve a specific goal.
Classes and Objects
Classes are user-defined data types in C++ that define properties and behaviors of objects. Objects are instances of classes.
Inheritance
Inheritance allows a class to inherit properties and behaviors from another class. It promotes code reusability and helps in creating a hierarchical relationship between classes.
Polymorphism
Polymorphism is the ability for objects of different classes to respond to the same message or function call in different ways.
Encapsulation
Encapsulation refers to the bundling of data and methods that operate on that data into a single unit called an object. It helps in data hiding and protecting the integrity of the data.
Abstraction
Abstraction is the process of hiding the complex implementation details and showing only the necessary features of an object.
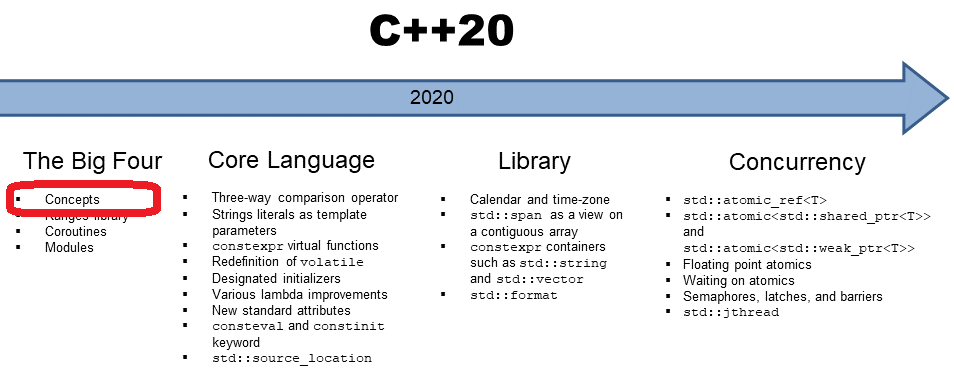
Architecture & How It Works
In C++, the source code is compiled into machine code by the compiler. This machine code is then executed by the computer’s processor.
Key Components:
- Source Code: The human-readable code written by the programmer.
- Compiler: Translates the source code into machine code.
- Linker: Combines multiple object files into an executable program.
- Loader: Loads the executable program into memory for execution.
Installation & Getting Started
To start programming in C++, follow these steps:
Step 1: Install a C++ compiler
Choose a C++ compiler suitable for your operating system. Some popular choices include:
- g++ for Linux
- Clang for macOS
- MinGW for Windows
Step 2: Write your first C++ program
Create a new C++ source file, such as hello.cpp, and write a simple program to display “Hello, World!”:
#include <iostream>
int main() {
std::cout << "Hello, World!" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Step 3: Compile and run your program
Compile your program using the chosen compiler, then run the executable to see the output.

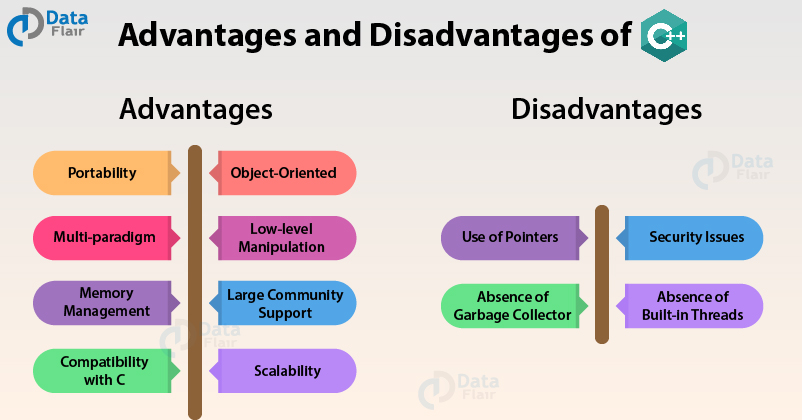
Benefits & Limitations of C++
Benefits
- High performance
- Strongly typed
- Supports object-oriented programming
- Provides low-level access to memory
Limitations
- Complex syntax
- Memory management can be challenging
- Lack of garbage collection
Real-World Use Cases of C++
C++ is a versatile programming language that is widely used in various industries for different applications, including:
- System Software Development: C++ is often used for developing system software such as operating systems, device drivers, and compilers due to its low-level capabilities.
- Game Development: Many popular games are developed using C++ because of its high performance and efficiency in handling graphics and complex game logic.
- Financial Systems: C++ is used in developing high-frequency trading systems, risk management tools, and other financial applications due to its speed and reliability.
- Embedded Systems: C++ is popular for developing embedded systems in industries like automotive, aerospace, and IoT due to its ability to directly interact with hardware.

Best Practices & Recommendations of C++
When working with C++, it is important to follow certain best practices to ensure code quality and maintainability.
Some recommendations include:
- Use modern C++ features: Take advantage of the latest language features and standard libraries to write cleaner and more efficient code.
- Follow naming conventions: Adopt consistent naming conventions for variables, functions, classes, and other identifiers to improve code readability.
- Avoid raw pointers: Prefer smart pointers and RAII (Resource Acquisition Is Initialization) over raw pointers to manage memory safely and efficiently.
- Use const and constexpr: Use const for variables that should not be modified and constexpr for computations that can be evaluated at compile time.
- Write modular and reusable code: Divide your code into smaller, reusable modules and classes to promote code reusability and maintainability.

Comparison with Alternatives of C++
When it comes to programming languages, C++ is often compared with other languages to understand its strengths and weaknesses. Here are some key points to consider:
Advantages of C++ over other languages:
- Performance: C++ is known for its high performance and efficiency, making it a preferred choice for system-level programming.
- Control over hardware: C++ allows developers to have more control over hardware-level interactions compared to languages with higher abstraction.
Disadvantages of C++ compared to other languages:
- Complexity: C++ can be more complex and challenging to learn compared to some modern programming languages.
- Memory management: Manual memory management in C++ can lead to memory leaks and other issues if not handled properly.
