Introduction & Overview
Retry logic is a critical mechanism in Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) to enhance the resilience and reliability of distributed systems. It involves automatically retrying failed operations, such as network requests or service calls, to mitigate transient failures and ensure system stability. This tutorial provides an in-depth exploration of retry logic, its architecture, implementation, and real-world applications in SRE.
What is Retry Logic?
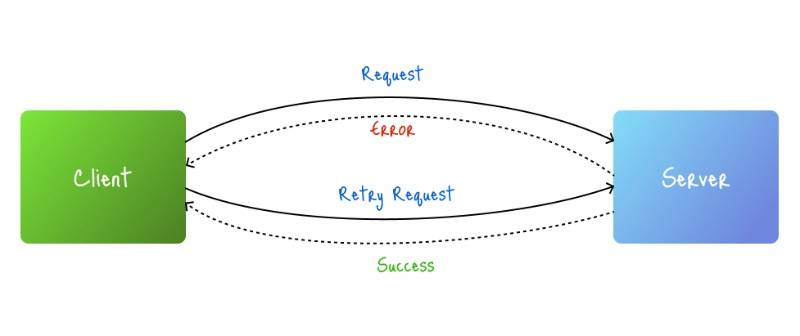
Retry logic is a fault-tolerance strategy where a system automatically reattempts a failed operation after a defined interval, typically to handle transient issues like network timeouts, temporary service unavailability, or resource contention. It is foundational in building robust systems that can self-heal from intermittent failures.
History or Background
Retry logic emerged with the rise of distributed systems in the early 2000s, particularly in cloud computing and microservices architectures. As systems became more complex, transient failures became common, necessitating automated recovery mechanisms. Early implementations were ad hoc, but frameworks like Netflix’s Hystrix and AWS SDKs formalized retry patterns, integrating them into modern SRE practices.
Why is it Relevant in Site Reliability Engineering?
In SRE, retry logic is vital for:
- Reducing Downtime: Automatically recovers from transient failures without manual intervention.
- Improving User Experience: Minimizes disruptions by retrying failed requests transparently.
- Scalability: Supports distributed systems by handling failures gracefully.
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces the need for over-provisioning resources to handle transient issues.
Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Transient Failure | Temporary issues like network glitches or service overloads that resolve quickly. |
| Retry Policy | Rules defining the number of retries, delay between attempts, and conditions for retrying. |
| Backoff Strategy | A method to increase delay between retry attempts, often exponentially, to avoid overwhelming systems. |
| Circuit Breaker | A pattern that halts retries after repeated failures to prevent cascading issues. |
| Idempotency | Ensuring operations can be safely retried without unintended side effects. |
How it Fits into the Site Reliability Engineering Lifecycle
Retry logic integrates into multiple SRE phases:
- Design: Engineers define retry policies during system architecture planning.
- Implementation: Retry mechanisms are coded into services or leveraged via libraries.
- Monitoring: Metrics track retry success rates and failure patterns.
- Incident Response: Retries reduce the need for manual intervention during transient failures.
- Postmortems: Analysis of retry logs helps identify root causes of failures.
Architecture & How It Works
Components
Retry logic typically involves:
- Client: Initiates the request (e.g., an application or microservice).
- Retry Handler: Manages retry attempts, including policy enforcement and backoff logic.
- Target Service: The external system or API being called.
- Logging/Monitoring: Captures retry attempts and outcomes for observability.
Internal Workflow
- Request Initiation: The client sends a request to the target service.
- Failure Detection: The retry handler identifies a failure (e.g., HTTP 503 or timeout).
- Policy Check: The handler evaluates the retry policy (e.g., max attempts, delay).
- Backoff Application: Applies a delay (e.g., exponential backoff) before retrying.
- Retry Execution: Reattempts the request until success or policy limits are reached.
- Result Handling: Returns success or failure to the client, with logs for monitoring.
Architecture Diagram Description
The architecture can be visualized as:
- Client: Sends requests to the retry handler.
- Retry Handler: A middleware layer with a retry policy (e.g., 3 attempts, exponential backoff). It communicates with the target service and logs outcomes to a monitoring system.
- Target Service: The external API or service, potentially in a cloud environment.
- Monitoring System: Collects retry metrics (e.g., Prometheus or CloudWatch).
- Flow: Client → Retry Handler → Target Service; logs flow to Monitoring System.
┌─────────────┐
Request │ Client │
────────▶│ Service │
└──────┬──────┘
│ Failure
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Retry Logic │
│ (Handler) │
└──────┬──────┘
│ Backoff + Jitter
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Service │
└──────┬──────┘
│ Success/Failure
▼
┌─────────────┐
│ Monitoring │
│ & Logs │
└─────────────┘
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: Retry logic can be embedded in deployment pipelines (e.g., Jenkins, GitHub Actions) to handle transient failures in tests or deployments.
- Cloud Tools: AWS SDKs, Google Cloud Client Libraries, and Azure SDKs provide built-in retry mechanisms. For example, AWS SDKs allow configuring retry policies for S3 or DynamoDB calls.
Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
- Programming Language: Python, Java, or Node.js (examples use Python).
- Libraries: Use
requests(Python) or similar HTTP libraries with retry support. - Monitoring: Prometheus or a cloud-native monitoring tool.
- Environment: A cloud environment (e.g., AWS, GCP) or local setup with Docker.
Hands-on: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
Below is a Python example using the requests library with tenacity for retry logic.
- Install Dependencies:
pip install requests tenacity2. Create a Retry Policy:
from tenacity import retry, stop_after_attempt, wait_exponential, retry_if_exception_type
import requests
from requests.exceptions import RequestException
@retry(
stop=stop_after_attempt(3),
wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=1, min=2, max=10),
retry=retry_if_exception_type(RequestException)
)
def make_request(url):
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()3. Test the Retry Logic:
try:
result = make_request("https://api.example.com/data")
print(result)
except Exception as e:
print(f"Failed after retries: {e}")4. Monitor Retries:
Add logging to track retry attempts:
from tenacity import after_log
import logging
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
@retry(
stop=stop_after_attempt(3),
wait=wait_exponential(multiplier=1, min=2, max=10),
retry=retry_if_exception_type(RequestException),
after=after_log(logging.getLogger(), logging.INFO)
)
def make_request(url):
response = requests.get(url)
response.raise_for_status()
return response.json()Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: API Call Reliability
A microservices-based e-commerce platform experiences intermittent API failures due to network latency. Retry logic is implemented to retry failed checkout requests, ensuring users can complete purchases without errors.
Scenario 2: Database Connection Resilience
In a financial application, transient database connection issues occur during peak load. Retry logic in the application layer retries failed queries, reducing downtime and manual intervention.
Scenario 3: Cloud Service Integration
An SRE team managing a cloud-based analytics platform uses retry logic in AWS Lambda functions to handle transient S3 bucket access failures, ensuring data processing pipelines remain operational.
Industry-Specific Example: Healthcare
In healthcare systems, retry logic ensures reliable communication between patient monitoring devices and cloud servers, retrying failed data uploads to prevent loss of critical health metrics.
Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Improved Reliability: Handles transient failures automatically.
- Reduced Manual Intervention: Minimizes SRE team workload.
- Scalability: Supports high-availability systems in cloud environments.
- Cost Savings: Avoids over-provisioning for transient issues.
Common Challenges or Limitations
- Overloading Systems: Improperly configured retries can amplify failures (e.g., retry storms).
- Non-Idempotent Operations: Retrying non-idempotent requests can cause unintended side effects.
- Complexity: Requires careful tuning of retry policies and backoff strategies.
- Latency: Retries introduce delays, impacting user experience.
Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Ensure operations are idempotent to prevent duplicate actions.
- Use secure retry policies with exponential backoff to avoid overwhelming services.
- Validate inputs to prevent retrying malicious or malformed requests.
Performance
- Tune retry delays to balance responsiveness and system load.
- Use circuit breakers to halt retries during prolonged failures.
- Monitor retry metrics to identify patterns and optimize policies.
Maintenance
- Regularly review retry logs to detect recurring failures.
- Update retry policies based on system performance and failure rates.
Compliance Alignment
- Ensure retry logic complies with data protection regulations (e.g., GDPR, HIPAA) by securing retry data.
- Log retry attempts in compliance with audit requirements.
Automation Ideas
- Integrate retry logic into CI/CD pipelines to handle transient test failures.
- Use infrastructure-as-code (e.g., Terraform) to define retry policies for cloud services.
Comparison with Alternatives
| Feature | Retry Logic | Circuit Breaker | Rate Limiting |
|---|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Retries transient failures | Halts requests during failures | Controls request frequency |
| Use Case | API calls, database queries | Preventing cascading failures | Protecting APIs from abuse |
| Complexity | Moderate | High | Low |
| When to Use | Transient failures are common | Prolonged failures expected | High traffic or DoS risk |
When to Choose Retry Logic
- Use retry logic for transient, short-lived failures in distributed systems.
- Opt for circuit breakers when failures are prolonged or cascading.
- Combine with rate limiting for APIs under heavy load.
Conclusion
Retry logic is a cornerstone of resilient system design in SRE, enabling automatic recovery from transient failures. By carefully designing retry policies, integrating with monitoring tools, and following best practices, SRE teams can enhance system reliability and user experience. Future trends include AI-driven retry optimization and tighter integration with observability platforms.
Resources
- Official Docs: Tenacity Library, AWS SDK Retry
- Communities: SRE forums on Reddit, CNCF Slack, and X posts on #SRE and #RetryLogic.