Introduction & Overview
Root Cause Analysis (RCA) is a systematic process used to identify the underlying causes of incidents, outages, or performance issues in systems. In Site Reliability Engineering (SRE), RCA is critical for ensuring system reliability, minimizing downtime, and improving service quality. This tutorial provides an in-depth exploration of RCA, tailored for SRE practitioners, with practical guidance, real-world examples, and best practices.
What is Root Cause Analysis (RCA)?
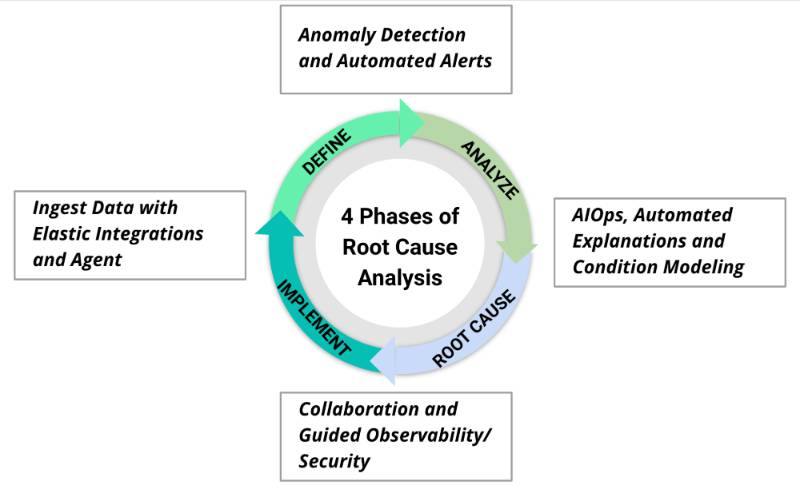
RCA is a problem-solving methodology that seeks to identify the primary cause(s) of an incident rather than merely addressing its symptoms. In SRE, RCA is used to analyze system failures, understand contributing factors, and implement preventive measures.
- Purpose: To prevent recurrence of incidents by addressing root causes.
- Scope: Applies to software, hardware, process, or human-related issues.
- Outcome: Actionable insights and solutions to enhance system reliability.
History or Background
RCA originated in industries like manufacturing and aviation, notably with techniques like the “5 Whys” developed by Sakichi Toyoda in the 1930s for Toyota’s production system. In the context of SRE, RCA evolved with the rise of distributed systems and cloud computing, where complex, interconnected systems required structured analysis to diagnose failures. Google’s SRE practices, formalized in the early 2000s, popularized RCA in tech, emphasizing blameless postmortems.
Why is it Relevant in Site Reliability Engineering?
In SRE, where uptime and performance are paramount, RCA helps:
- Reduce Mean Time to Recovery (MTTR): By quickly identifying and resolving root causes.
- Improve System Resilience: Through preventive measures based on RCA findings.
- Foster Collaboration: Encourages cross-functional teams to analyze incidents blamelessly.
- Support SLOs/SLAs: Ensures service level objectives and agreements are met by minimizing recurring issues.
Core Concepts & Terminology
Key Terms and Definitions
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Incident | An unplanned event causing disruption to a service or system. |
| Root Cause | The primary factor(s) that, if corrected, prevents the incident from recurring. |
| Blameless Postmortem | A collaborative RCA process focusing on system improvements, not individual blame. |
| Causal Factor | Events or conditions contributing to an incident, not necessarily the root cause. |
| Mitigation | Temporary measures to reduce the impact of an incident. |
| Corrective Action | Permanent solutions addressing the root cause. |
How RCA Fits into the SRE Lifecycle
RCA is integral to the SRE lifecycle, particularly in the incident response and post-incident analysis phases:
- Incident Detection: Monitoring tools (e.g., Prometheus, Datadog) detect anomalies.
- Response: On-call engineers mitigate the issue to restore service.
- RCA Execution: Post-incident, teams analyze logs, metrics, and timelines to identify root causes.
- Preventive Measures: Implement changes to prevent recurrence, such as code fixes or process improvements.
- Continuous Improvement: RCA insights feed into system design and automation.
Architecture & How It Works
Components and Internal Workflow
RCA in SRE involves a structured process with the following components:
- Data Collection: Logs, metrics, traces, and incident timelines.
- Analysis Tools: Visualization platforms (e.g., Grafana), log aggregators (e.g., ELK Stack), or custom scripts.
- Collaboration Platforms: Tools like Slack, Jira, or Confluence for team coordination.
- Documentation: Postmortem reports capturing findings and action items.
Workflow:
- Incident Identification: Define the scope and impact of the incident.
- Timeline Construction: Build a chronological sequence of events using logs and metrics.
- Causal Analysis: Use techniques like 5 Whys or Fishbone diagrams to trace causes.
- Root Cause Identification: Distinguish between symptoms and root causes.
- Action Planning: Propose corrective actions and prioritize based on impact.
- Implementation and Monitoring: Deploy fixes and monitor for effectiveness.
Architecture Diagram
Since images cannot be directly included, the RCA architecture can be described as follows:
- Input Layer: Monitoring systems (Prometheus, CloudWatch) and logging tools (Splunk, Loki) feed incident data.
- Processing Layer: Analysis tools (Grafana, Kibana) and RCA frameworks (5 Whys, Fishbone) process data.
- Collaboration Layer: Teams use communication tools (Slack, PagerDuty) to discuss findings.
- Output Layer: Postmortem reports and action items stored in documentation platforms (Confluence, Notion).
- Feedback Loop: Corrective actions are integrated into CI/CD pipelines or infrastructure-as-code (IaC) tools.
┌────────────────────┐
│ Incident Event │
└───────┬────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Incident Detection │
│ (Monitoring/Alerts) │
└─────────┬──────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────┐
│ Incident Response │
│ (Mitigation) │
└─────────┬──────────┘
│
▼
┌────────────────────────────────┐
│ Root Cause Analysis (RCA) │
│ - Collect logs & metrics │
│ - Apply RCA methods (5 Whys) │
│ - Identify systemic failures │
└───────────┬────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌──────────────────────┐
│ Postmortem & Actions │
└───────────┬─────────┘
│
▼
┌──────────────────────┐
│ Continuous Improvement│
└──────────────────────┘
Integration Points with CI/CD or Cloud Tools
- CI/CD: RCA findings can trigger automated tests or deployment rollbacks via tools like Jenkins or GitLab CI.
- Cloud Tools: Integrates with AWS CloudTrail, Azure Monitor, or GCP Stackdriver for log and metric analysis.
- Automation: Tools like Terraform or Ansible implement infrastructure changes based on RCA outcomes.
Installation & Getting Started
Basic Setup or Prerequisites
To perform RCA in an SRE context, you need:
- Monitoring Tools: Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog for metrics.
- Logging Systems: ELK Stack, Splunk, or Cloud-native logging (e.g., AWS CloudWatch).
- Collaboration Tools: Slack, Jira, or Confluence for team coordination.
- Access to Systems: Permissions to access production logs, metrics, and infrastructure.
- Basic Knowledge: Familiarity with SRE principles and incident response.
Hands-on: Step-by-Step Beginner-Friendly Setup Guide
Below is a guide to set up a basic RCA process using open-source tools like Prometheus, Grafana, and the ELK Stack.
- Install Prometheus for Monitoring:
- Deploy Prometheus on a server or cloud instance.
wget https://github.com/prometheus/prometheus/releases/download/v2.45.0/prometheus-2.45.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
tar xvfz prometheus-2.45.0.linux-amd64.tar.gz
cd prometheus-2.45.0.linux-amd64
./prometheus --config.file=prometheus.ymlConfigure prometheus.yml to scrape metrics from your application.
2. Set Up Grafana for Visualization:
- Install Grafana and connect it to Prometheus.
sudo apt-get install -y grafana
sudo systemctl start grafana-serverAccess Grafana at http://<server-ip>:3000, add Prometheus as a data source, and create dashboards.
3. Configure ELK Stack for Logging:
- Install Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana.
docker run -d --name elasticsearch -p 9200:9200 elasticsearch:8.8.0
docker run -d --name kibana -p 5601:5601 kibana:8.8.0- Configure Logstash to ingest application logs.
4. Conduct a Sample RCA:
- Simulate an incident (e.g., high latency).
- Use Grafana to identify spikes in metrics.
- Query logs in Kibana to trace the issue.
- Document findings in a postmortem template (e.g., in Confluence).
Real-World Use Cases
Scenario 1: Application Outage Due to Database Overload
- Context: A web application experiences downtime during peak traffic.
- RCA Process:
- Data Collection: Query database logs in CloudWatch and metrics in Prometheus.
- Analysis: Identify a spike in database queries causing resource exhaustion.
- Root Cause: Unoptimized SQL queries lacking indexes.
- Corrective Action: Add indexes and implement query caching.
- Industry Example: E-commerce platforms during Black Friday sales.
Scenario 2: Microservice Failure in a Distributed System
- Context: A microservice fails, causing cascading failures.
- RCA Process:
- Timeline: Trace service dependencies using Jaeger.
- Analysis: Identify a misconfigured API rate limit.
- Root Cause: Incorrect rate-limiting logic in the service configuration.
- Corrective Action: Update configuration and add automated tests.
- Industry Example: Streaming services like Netflix.
Scenario 3: Human Error in Deployment
- Context: A faulty deployment causes service disruption.
- RCA Process:
- Data: Review CI/CD pipeline logs in Jenkins.
- Analysis: Identify a manual configuration error.
- Root Cause: Lack of automated validation in the deployment pipeline.
- Corrective Action: Implement pre-deployment checks.
- Industry Example: Financial institutions with strict compliance requirements.
Scenario 4: Network Latency in Cloud Infrastructure
- Context: Users report slow response times.
- RCA Process:
- Data: Analyze network metrics in AWS CloudTrail.
- Analysis: Detect a misconfigured load balancer.
- Root Cause: Incorrect health check settings.
- Corrective Action: Update load balancer configuration.
- Industry Example: SaaS providers like Salesforce.
Benefits & Limitations
Key Advantages
- Proactive Problem Solving: Prevents recurring incidents.
- Improved Collaboration: Encourages cross-team accountability via blameless postmortems.
- Data-Driven Decisions: Leverages metrics and logs for objective analysis.
- Scalability: Applicable to both small and large-scale systems.
Common Challenges or Limitations
| Challenge | Description | Mitigation |
|---|---|---|
| Complexity | Large systems make root cause identification difficult. | Use distributed tracing tools (e.g., Jaeger). |
| Time-Intensive | RCA can delay recovery if not prioritized. | Balance mitigation and analysis. |
| Human Bias | Blaming individuals can skew analysis. | Adopt blameless postmortem culture. |
| Tool Dependency | Requires robust monitoring and logging. | Invest in observability tools. |
Best Practices & Recommendations
Security Tips
- Access Control: Restrict access to logs and metrics to authorized personnel.
- Data Privacy: Anonymize sensitive data in RCA reports.
- Audit Trails: Maintain logs of RCA processes for compliance.
Performance
- Automate Data Collection: Use tools like Fluentd to streamline log aggregation.
- Prioritize Metrics: Focus on key performance indicators (KPIs) like latency and error rates.
Maintenance
- Regular Reviews: Schedule periodic RCA process audits.
- Update Tools: Keep monitoring and logging tools up to date.
Compliance Alignment
- Align RCA with standards like ISO 27001 or SOC 2 by documenting findings and corrective actions.
- Use templates to ensure consistency in postmortem reports.
Automation Ideas
- Automate incident detection with alerting tools (e.g., PagerDuty).
- Integrate RCA outcomes into CI/CD pipelines for automated testing.
Comparison with Alternatives
| Approach | Description | Pros | Cons | When to Choose RCA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCA | Systematic analysis of root causes. | Prevents recurrence, data-driven. | Time-intensive, requires expertise. | Complex incidents requiring deep analysis. |
| Quick Fixes | Immediate symptom mitigation. | Fast resolution. | Doesn’t address root causes. | Minor, non-recurring issues. |
| Automated Rollbacks | Revert to previous system state. | Minimizes downtime. | No learning or prevention. | Deployment-related incidents. |
| Log Analysis Alone | Review logs without structured RCA. | Simple, quick. | Misses systemic issues. | Initial troubleshooting. |
When to Choose RCA:
- For recurring or high-impact incidents.
- When long-term reliability is a priority.
- In complex systems with multiple dependencies.
Conclusion
RCA is a cornerstone of SRE, enabling teams to transform incidents into opportunities for system improvement. By systematically identifying root causes and implementing corrective actions, organizations can enhance reliability, meet SLOs, and foster a culture of continuous improvement. As systems grow more complex with cloud-native architectures, RCA will evolve with AI-driven analysis and automation.
Next Steps:
- Start with a simple RCA process using open-source tools.
- Join SRE communities (e.g., SREcon, Reddit’s r/sre).
- Explore advanced techniques like causal inference.
Resources:
- Official SRE Book by Google: https://sre.google/sre-book/
- Prometheus Documentation: https://prometheus.io/docs/
- ELK Stack Guide: https://www.elastic.co/guide/